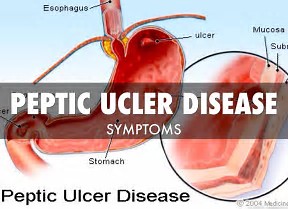
Peptic Ulcer
Peptic ulcer is a general term that refers to ulcers occurring in the lower esophagus, the stomach, or the duodenum (upper part of the small intestine).
What is the difference between a duodenal ulcer and a gastric ulcer?
A duodenal ulcer is a break in the lining of the upper part of the small intestine (the duodenum): a gastric ulcer is a break in the lining of the stomach.
what causes duodenal and gastric ulcers?
Duodenal ulcers are much more common than gastric ulcers. The primary cause of duodenal ulcers is increase production of acid by the stomach; factors that may contribute to this include cigarette smoking, excessive alcohol intake, chronic emotional stress, and certain drugs (aspirin, antiinflamitory drugs, and corticosteroids). Gastric ulcers, on the other hand, are thought to be caused by changes in the stomach lining that makes it more susceptible to damage by the acid normally produced by the stomach. The stomach lining may be damaged by chronic gastric gastritis, reflux of bile, and the same drugs that cause increased acid production. Recent research has shown that an infectious organism frequently plays a contributing role in both duodenal and gastric ulcer development.
What are the symptoms of ulcers?
Duodenal ulcers are characterized by pain that occurs when the stomach is empty and is relieved by eating ; the pain usually is in the midabdominal area. Vomiting may occur but is uncommon.Some people have mild diarrhea with black stool (black stool indicates the presence of blood). Symptoms of a gastric ulcers include pain, a feeling of fullness, nausea, and vomiting. The pain is not necessary relieved by eating; in fact, it may become worse after eating. The pain is located in the upper abdomen, either in the middle or to the left. If vomiting occurs, the vomit may be streaked with blood. Later symptoms include fatigue and weight loss. Attacks of pain caused by an ulcer are subject to remission, and the pain may absent for some weeks or months (this is particularly true of duodenal ulcers). Pain seems to depend on inflammation of the ulcer and not merely on its presence
What are the possible complications?
Chronic slow bleeding can cause your stool to look dark (Tarry); over time, slow bleeding can cause anemia and fatigue. Sudden major bleeding can cause you to vomit large amounts of blood or to pass bloody stools. Major bleeding requires prompt treatment. ( Major bleeding is more likely to occur in a patient who had ulcer symptoms for a long time). Other, uncommon complications that may occur include perforation and obstruction. Perforation means that the ulcer erodes through the wall of the stomach or the duodenum; this creates a hole that allows stomach or intestinal content to leak into the abdominal. Perforation causes severe abdominal pain and necessitates immediate treatment. Obstruction occurs when there is scarring or swelling that blocks passage of the food and digestive juices from the stomach into the small intestines. This causes persistent vomiting, and medical treatment is required.
How are ulcers treated and managed?
Many peptic ulcers heal spontaneously, but medical treatment usually is required. Medical treatment usually involves the following:
- Eliminating the use of aspirin, antinflammatory medications, and corticosteroids.
- Taking antacids (to Neutralize acid) and "anti ulcer" drugs such as Tagamet or Zantac (to reduce the amount of acid produced and promote healing)
- Eliminate foods and beverages that cause pain or delay healing (e.g.., alcohol may delay healing)
- Taking steps to reduce or more effectively manage stressful situations.
Antibiotics may be used to treat resistant or recurrent ulcer disease. Because the symptoms sometimes disappear before the ulcer has completely healed, some ulcer patients give up before the course of treatment has been completed. It is essential to follow your doctor's instructions, if medical treatment is to succeed. Malignant changes sometimes occur in gastric ulcers , but these changes can be diagnosed only through specific tests. Thus it is foolish to try to cure ulcers by yourself or to ignore ulcer symptoms in the hope that the condition will get better by itself. It is important to obtain medical evaluation and advice in treating ulcer symptoms.
